ZERO WASTE TO LANDFILL
The steel manufacturing process generates various forms of by-products. Some of these materials, which were historically considered waste, are now valuable products. Other by-products are reused or recycled within the iron and steelmaking process or by partners in other industrial sectors. The Company is also working to explore new opportunities for reusing and recycling by-product material.
Good waste management practices have extensive environmental and economic benefits. The Company continues to investigate ways to achieve zero waste to landfill or incineration.
Steel: 100% Recyclable
Steel is not only 100 per cent recyclable but can also be repeatedly recycled without a loss of key properties, a characteristic that can be claimed by very few materials. If steel is recovered at the end of its use, its lifecycle continues.
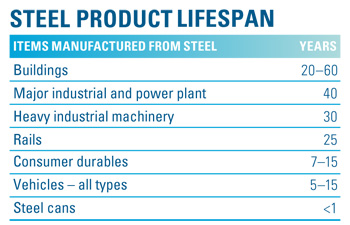
Recycling prevents the waste of potentially useful materials, reduces consumption of raw materials and energy, and reduces pollution. There is a long-established and competitive global market for scrap and recovered steel for recycling. Because steel products generally have a long lifespan, the steel available for recycling today may have been produced many decades ago. The following table provides some examples of the average life of items made mainly from steel.
Due to its magnetic properties, steel is relatively easy to separate from waste streams enabling higher rates of recovery than all comparable materials.
Scrap steel is an essential feed material in the integrated steelmaking processes used at Port Kembla Steelworks and New Zealand Steel, and also the electric arc furnace process used at the North Star BlueScope Steel plant in Delta, Ohio, USA.
During FY2011 the Company externally sourced and recycled over 1.27 million tonnes of steel scrap.
Current controls
BlueScope Steel’s waste management strategies are based on the Waste Hierarchy designed to minimise waste generation and extract the maximum practical benefits from by-products.
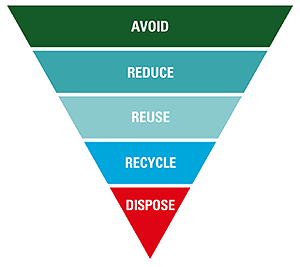
Some examples include:
Process dusts and sludges, which contain iron, can be recycled in the Company’s iron or steelmaking process.
Granulated Slag, is used extensively in the cement industry, reducing the need to extract virgin limestone and avoiding greenhouse gas emissions, which occur when this material is calcinated into quicklime.
BlueScope Steel cooperates with downstream users of by-products to improve by-product quality and increase their use.
Performance
Material efficiency is a measure of how efficiently a company uses raw materials to produce its products and by-products. The indicator measures the amount of by-product material that is reused, sold or recycled, relative to total crude steel production.
The maximum theoretical material efficiency (100%) would require all raw materials to be ultimately processed into saleable products or by-products. Over 96 per cent material efficiency was achieved in FY2011 and more than 2 million tonnes of by-products were sold for a wide variety of uses.
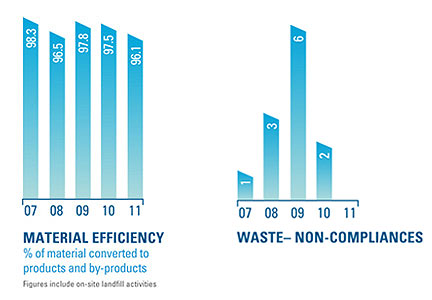
Compliance with waste legislation at each of our sites is important. Waste legislation can involve classifying the waste, on site waste storage and ensuring the waste arrives at the appropriate waste facility. The large majority of BlueScope Steel’s waste related non-compliances are minor in nature. There were no waste non-compliances for FY2011, an improvement on previous years.

